Introduction
A fleet manager is a professional who oversees the operation and maintenance of company vehicles. This can include cars, trucks, vans, and other vehicles used by the organisation for business purposes. The role is critical to the success of any company that relies on vehicles to conduct business. In this blog post, we will discuss his/her key responsibilities of a fleet manager and why having a professional in this role is essential.
The Role of a Fleet Manager
The primary responsibility of a fleet manager is to ensure that the company’s vehicles are operating efficiently and are well-maintained. This includes managing the entire lifecycle of the vehicles, from acquisition to disposal. Here are some of the specific tasks she/he is responsible for:
- Establishing vehicle offering: This involves research and selection suppliers, and the purchase of new vehicles for the company’s fleet. Factors such as cost, fuel efficiency, safety, and brand/model attractiveness should be considered, when choosing new vehicles.
- Operational fleet processes: ensuring that all fleet processes run smoothly. This includes ordering, short-term rentals, new charging or fuel cards, damage reports, driver license checks, and so forth.
- Fleet metric tracking and data analysis: monitor suppliers, insurance claims, fuel consumption, and other data related to the different vehicles in their fleet. This data is used to identify areas where improvements can be made, such as setting up driver incentives to reduce fuel consumption or implement safety programs, such as defensive driving courses, to reduce the risk of accidents.
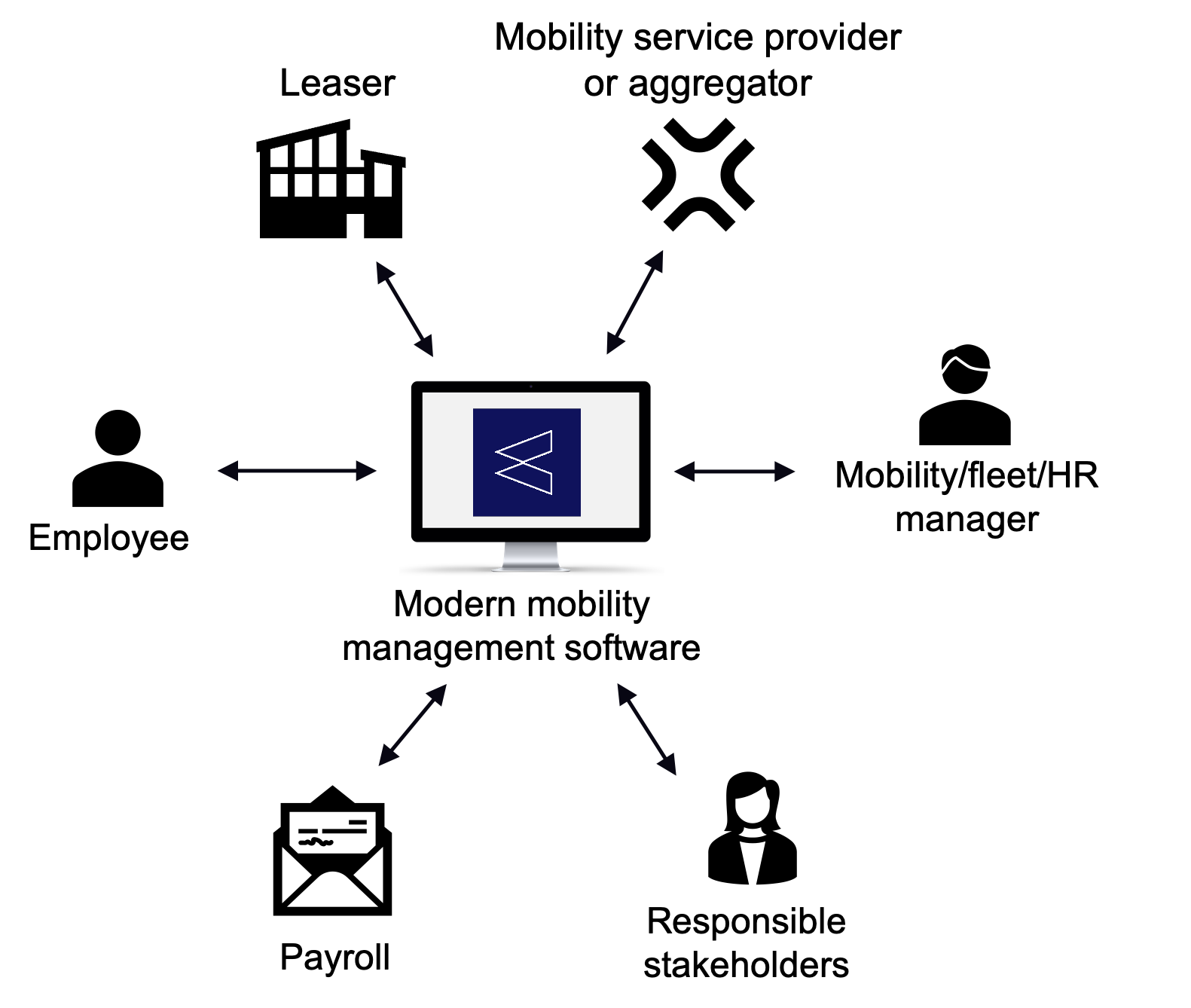
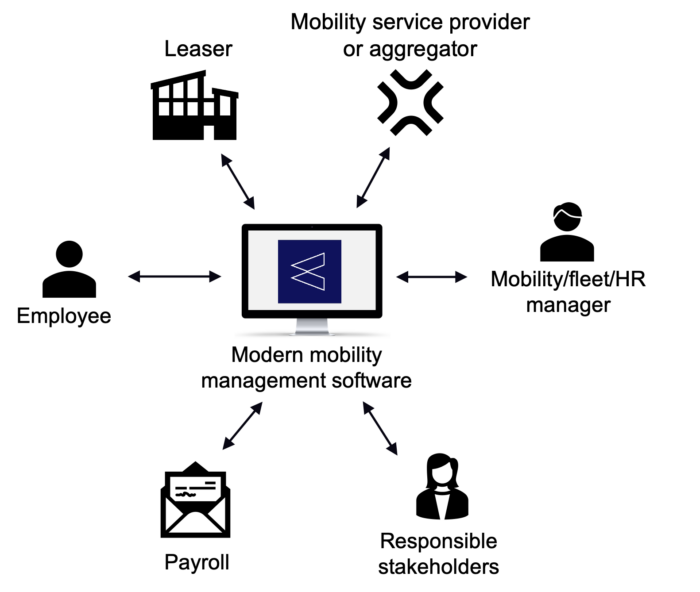
- Communication hub: ensuring that all drivers are properly served, and to ensure they follow the policy and procedures when ordering and operating or driving company vehicles. They may are the intermediate actor between leasing companies, management, employees, and other stakeholders
- Cost Control: Fleet managers must work within a budget to ensure that the company’s vehicle expenses are kept under control. This includes monitoring fuel costs, maintenance expenses, and other costs associated with operating the fleet.

The Changing Role of a Fleet Manager
Advancements in software technology and motor types are challenging fleet managers to enhance their skills. Software can automate current manual and labour-intensive processes, and allow for more strategic work. The job now increasingly demands software and data analysis capabilities, knowledge of fiscal regulations and strategic mobility thinking. In addition to traditional responsibilities, the evolving role requires the ability to:
- Strategic mobility policy making: Leverage trends and evolving employee preferences in terms of mobility. Consider how new legislation affects fleet operations, including fiscal measures related to internal combustion engine vehicles, as well as incentivises other forms of mobility, via e.g. a mobility budget.
- Data analysis and communication: Provide and communicate insights in a clear and effective way to different stakeholders, both internally and externally. Collaborate across departments: develop a carbon-reduction target with the sustainability manager, provide recommendations for budget control to finance departments, configure an attractive car policy within budget for HR, answer questions to drivers.
- Improve user experience: internal customer is king, and services to drivers should be low-threshold, with intuitive designs and responsive customer support. To keep up with these evolving demands, support structures should be put in place to guarantee employee satisfaction.
- Process optimisation: With digitalised processes, improving the internal process becomes an important task. Identify bottlenecks, long lead times and identify solutions for a better corporate mobility practice.
- Strategic supplier negotiations: because of digitalised processes, process data and pricing information can be leveraged to keep suppliers on their toes, by automatically monitoring their performance compared to their SLAs, and comparing performance via multi-bidding each car order. Negotiate with the best information available.
Conclusion
A fleet manager plays a critical role in the success of any company that relies on vehicles to conduct business or to attract employees. By overseeing the suppliers, budgets, and operation of the company’s vehicles, this role aims at helping to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and enhance safety. The right software can enable the fleet manager to reduct the manual hassle and focus on strategic, analytical work that can bring true value to the company.